On-page SEO: The Definitive Guide for 2023
In this guide, we will discuss the basics of on-page SEO, including:
- What is on-page SEO?
- Why is on-page SEO important?
- A checklist of on-page optimization elements and how to optimize them.
On-page SEO: The Definitive Guide for 2023
Table of Contents
What is On-page SEO?
On-page SEO, also referred to as “on-site SEO,” involves enhancing the content of web pages to make them more appealing to search engines and users. This includes factors such as the title tag, meta description, content, images, and internal links.
On-page SEO vs. Off-page SEO: What’s the difference?
On-page SEO emphasizes the optimization of website elements that are under your direct control, while off-page SEO primarily focuses on building external signals like backlinks that contribute to your website’s authority and reputation. Both approaches are important for a comprehensive SEO strategy and should be implemented together to achieve optimal results.
Why Is On-page SEO Important?
According to Google’s “How Search Works” report, search systems analyze various factors to determine the relevance of content and one key signal of relevance is the presence of keywords related to the search query within the webpage’s content, headings, and body text.

In other words, on-page optimization helps search engines better understand your website.
And these advantages bring about a multitude of benefits such as:
1. Increased Organic Traffic
The higher your website ranks in search engine results pages (SERPs), the more traffic you will receive from search engines. This is because most people only click on the first few results on the SERPs.
According to Ahrefs, the position 1 organic result on Google’s search engine results page receives 49% of all clicks and more than 99% of Google searchers only click on results on the 1st page. So, if you want to get traffic, you need to be near the top.
Additionally, websites that rank higher tend to experience significantly higher click-through rates (CTR). The first result in Google’s mobile search typically achieves an average organic CTR of 26.9%.
This means that if you can improve your website’s on-page SEO and rank higher in SERPs, you can significantly increase the amount of traffic your website receives.
2. Improved Brand Awareness
When your website is visible in search results, it will help to raise awareness of your brand. This is because people who are searching for products or services that you offer will be able to see your website in the results.
For example, if you are a business that sells shoes, and someone searches for “running shoes,” your website may appear in the results. If the person clicks on your website and finds it helpful, they will be more likely to remember your brand and consider buying from you in the future.
3. Increased Credibility
When your website is well-optimized for SEO, it will be seen as more credible by search engines and users. This is because search engines use a variety of factors to determine the credibility of a website, including the quality of the content, the use of keywords, and the overall structure of the website.
If your website is well-optimized for SEO, it will be seen as a high-quality website that is worth visiting. This can lead to more people trusting your website and its content.
Now that you’ve learnt why on-page SEO still matters, it’s time to start optimizing your content.
Elements of On-page Optimization and How to Optimize them?
Although there isn’t a universally recognized standard workflow for on-page optimization, it is crucial to conduct a thorough on-page audit to ensure that every opportunity is leveraged to enhance search engine rankings or achieve other key performance indicators (KPIs).
While improving the on-page aspects of a website may not have a straightforward, step-by-step guide, the following list aims to encompass all the commonly addressed on-page elements.
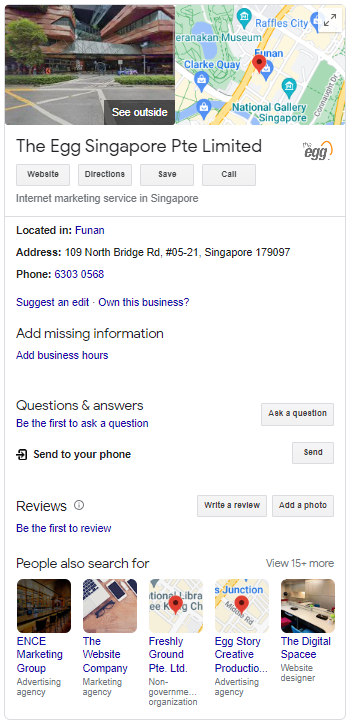
Meta Titles (Title Tags)
What are Meta Titles?
Meta titles, also known as title tags, are HTML elements that provide a concise and descriptive title for a web page. They are featured prominently on search engine results pages (SERPs) a clickable link and also appears in the browser window.
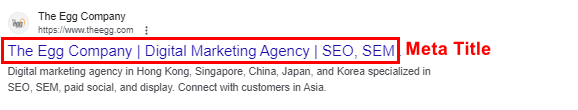
While the title tag alone may not have a significant impact on organic rankings, it is essential to understand that no single ranking factor holds a magical or overpowering influence. This is especially true when you’ve neglected the overall quality of your content or the importance of technical SEO.
Why Are Meta Titles (Title Tags) Important for SEO?
Title Tags Help Users and Search Engines Understand What Your Page Is About
Search engines like Google use meta titles as a ranking factor when determining the relevance and quality of a webpage. The presence of relevant keywords in your title tag helps search engines understand the main topic or theme of your page and when these keywords align with the user’s search query, your page will likely rank higher in the search results.
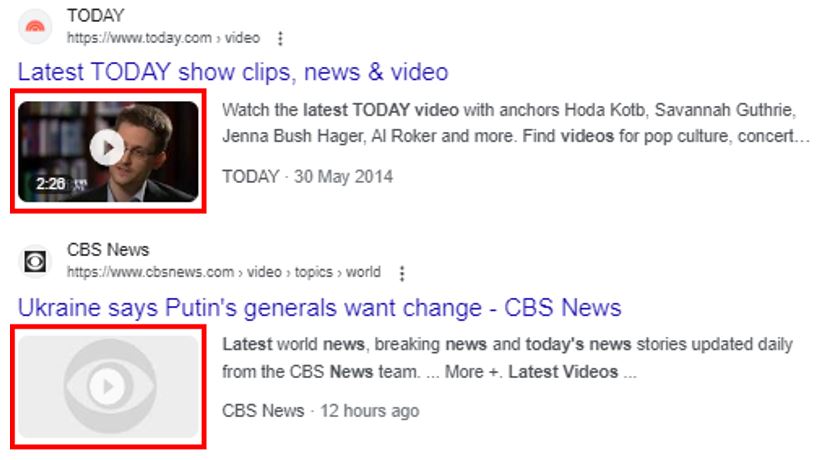
Title Tags help users decide whether or not to click on your search result link
The meta title provides a concise and informative summary of what users can expect to find on the page. By crafting a well-optimized title tag that accurately reflects the content of your page, you increase the likelihood of attracting the right audience and encouraging them to click on your link. This, in turn, improves the click-through rate (CTR) of your webpage, indicating to search engines that your page is relevant and valuable to users.
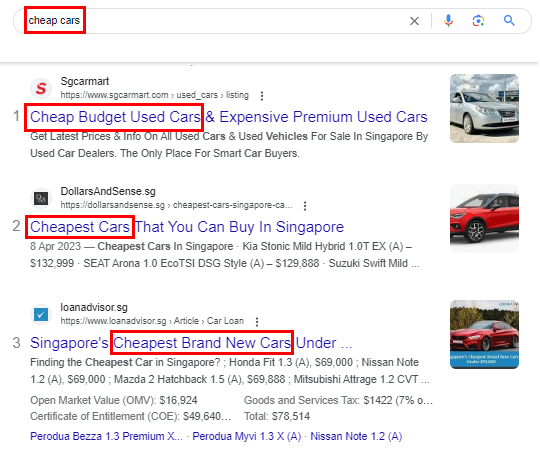
How to craft SEO-Friendly Meta Titles (Title Tags)?
Keep Title Tags Within 60 Characters
Keep your meta titles concise and to the point. Search engines typically display the first 60 characters, so make sure your most important information is within this limit. Shorter titles tend to have a higher click-through rate, as they are more likely to be fully visible on SERPs.
Include Relevant Keywords
Keywords are the foundation of SEO and incorporating them into your meta titles is crucial. Identify the relevant keywords that accurately describe the content of your page and integrate them naturally into your title tags. This helps search engines understand the relevance of your page to users’ search queries.
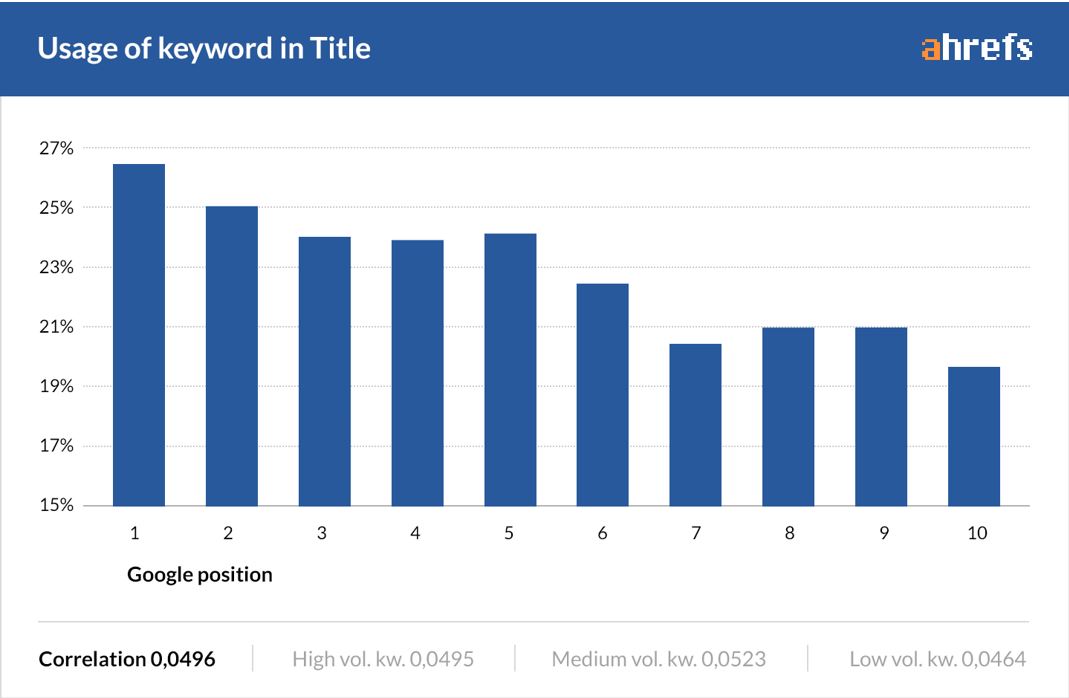
Ahrefs Study on correlation between usage of keywords in the title tag and rankings
Put Important Keywords First
Place your most important keywords at the beginning of your meta titles. Search engines place more weight on the first few words, so this ensures that the essential information is given priority. It also improves the visibility of your keywords on SERPs, increasing the likelihood of attracting clicks.
Do Not Duplicate Title Tags
Each page on your website should have a unique meta title. Duplicate title tags can confuse search engines and potentially harm your SEO efforts. Craft unique and descriptive titles for each page to ensure search engines can differentiate them and display the most relevant one in search results.
Do Not ‘Keyword Stuff’ Title Tags
While it’s important to include relevant keywords, avoid keyword stuffing at all costs. Keyword stuffing refers to the practice of overloading your meta titles with an excessive number of keywords in an unnatural manner. This can result in penalization from search engines and diminish the user experience. Focus on creating meaningful and compelling titles that accurately represent your content.
Make Your Headline (<H1> Tag) Different from The Title Tags
Differentiate your meta titles from the main headline of your page. The headline, marked with the <H1> HTML tag, appears directly on your webpage. It should complement the meta title by providing additional information and enticing users to explore further. This separation ensures that both elements serve their respective purposes effectively.
Don’t Put Your Company Name at The Front
Avoid placing your company name at the beginning of your meta titles. While it may be important to brand your website, search engines prioritize the relevance of the content to the user’s query. Including your company name can reduce the visibility of your targeted keywords and potentially make your titles less appealing to users.
Examples of good meta titles
Here are some examples of good meta titles:
- How to Write a Meta Title That Gets Clicks
- The Ultimate Guide to SEO for Beginners
- 10 Tips for Creating a Compelling Meta Title
- The Best Meta Title Generator for 2023
- How to Write a Meta Title That Converts
Why Is Google Rewriting My Title Tags?

A recent study conducted by Zyppy.com shows that Google rewrites page titles more than 60 percent of the time.
Understandably, this can be a frustrating experience for website owners and SEOs who invest considerable time and effort in crafting the perfect title tags. The changes made by Google varied in scope, ranging from minor alterations of a single word to a complete overhaul of the entire title tag.
So why does Google rewrite our Title Tags?
Too Short Or Too Long Titles
The ideal page title length is between 50-60 characters. If a page title is too long, Google may truncate it in the search results. This truncation can result in an incomplete or unclear representation of the page’s content, which can frustrate users and lead to a negative user experience.
To prevent this, Google may choose to rewrite the title tag, condensing it into a more concise form that fits within the character limit and effectively conveys the essence of the page.
Google Thinks There’s a More Suitable Title Tag for a Particular Query.
Google’s ultimate objective is to offer searchers the most effective and informative title tags that provide accurate context regarding the content of web pages. If a title tag fails to meet Google’s standards, its algorithm intervenes and modifies it accordingly.
Meta Descriptions
What are Meta Descriptions?
Meta descriptions are short snippets of text that provide a concise summary of the content on a webpage. They appear in the search engine results page (SERP) beneath the page title and URL. Meta descriptions serve as a preview of what users can expect to find on a particular webpage, acting like a pitch that convinces the user that the page is exactly what they’re looking for.
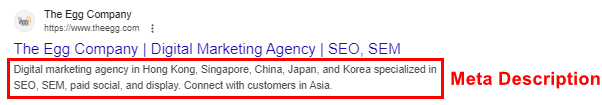
Why are Meta Descriptions Important For SEO?
Meta Descriptions act as “organic ad text” and have an impact on click-through-rate
A well-crafted meta description can entice users to click on your link by effectively showcasing the value and relevance of your content. It serves as an opportunity to differentiate your page from others in the search results and increase the likelihood of attracting clicks.
Meta Descriptions Appear in Search Engine Results Page (SERP)
When users search for specific keywords or phrases, search engines display a list of relevant results. The meta description, along with the page title, is what users see and use to evaluate which result is most relevant to their needs. By optimizing your meta descriptions, you can influence how users perceive your content and improve your visibility in the search results.
How To Write Great Meta Descriptions That Get Clicks?
Keep Meta Descriptions Within 160 Characters
Search engines usually display up to 160 characters of a meta description. Aim to keep your descriptions concise and compelling, providing enough information to pique interest without being cut off.
Include Relevant Keywords
Incorporate relevant keywords that align with the content on the webpage. These keywords help search engines understand the topic and context of your page, increasing the chances of your page appearing in relevant search queries.
Include A Call-To-Action
A call-to-action (CTA) is a powerful way to motivate users to take a specific action. By including a clear and persuasive CTA in your meta description, such as “Learn More,” “Discover,” or “Get Started,” you can encourage users to click through and engage with your content.
Make Sure It Matches The Content of The Page
Your meta description should accurately reflect the content users will find on the webpage. Misleading or irrelevant descriptions can result in a negative user experience and a high bounce rate. Aligning the meta description with the actual content helps set clear expectations and enhances user satisfaction.
Make Every Meta Description Unique
Each page on your website should have a unique meta description. This ensures that search engines can differentiate between different pages and display the most relevant description for each search query. It also provides an opportunity to optimize each meta description for different keywords and target specific user intent.
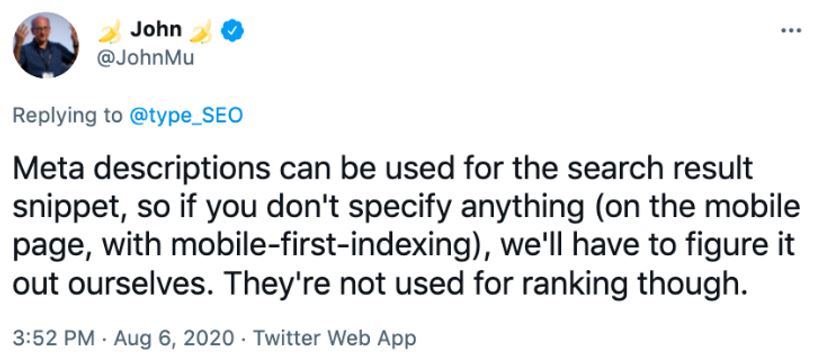
Are Meta Descriptions A Ranking Factor?
John Mueller clarifies that Meta Descriptions are not a ranking factor
Meta descriptions themselves are not a direct ranking factor in search engine algorithms. Google used to use meta descriptions as a ranking factor, but it found that they were not a reliable indicator of a page’s quality. For example, some webmasters would try to game the system by creating meta descriptions that were misleading or irrelevant to the content of the page.
However, meta descriptions play an essential role in influencing click-through rates (CTR) and user engagement, which indirectly affects SEO performance. When users see a well-crafted and relevant meta description in the search results, they are more likely to click on the link and visit the webpage.
Increased CTR can send positive signals to search engines, indicating that the page is relevant and valuable to users. This, in turn, can indirectly contribute to improved rankings over time.
Why Is Google Rewriting My Meta Descriptions?
According to a study by Portent, Google rewrites meta descriptions for pages over 70% of the time.
The study also notes that there’s a bump in the rate of meta descriptions rewrites from positions 4 to 6, which may be due to Google trying to boost relevance of those results.
This suggests that Google may be actively attempting to enhance the relevance of these results.
Poor Use of Meta Description
Google aims to provide users with the most relevant and informative search results. If your meta description doesn’t effectively summarize the content on your page or fails to provide useful information, Google may choose to rewrite it to better serve the user’s needs. This typically happens when your original meta description is too short, lacks detail, or is stuffed with irrelevant keywords.
Your meta description is too long
Google’s search results snippets are limited to 160 characters, so if your meta description is longer than that, Google may rewrite it to fit within the character limit.
Your meta description is not unique
If you have multiple pages on your site with the same meta description, Google may rewrite them to be more unique. This helps to ensure that the meta descriptions are accurate and relevant to the specific page that they are associated with.
Header Tags
What are Header Tags?
Header tags, also known as heading tags, are HTML elements used to separate headings and subheadings and provide structure to the content on a web page. These tags are not only important for organizing the content visually, but they also play a crucial role in search engine optimization (SEO) by helping search engines understand the context and relevance of the content.
Header Tag Levels
Header tags range from H1 to H6, with H1 being the most important and H6 being the least important.
- H1 – The primary heading of a page or post, typically centered around a specific keyword. Its purpose is to capture the reader’s attention and convey the main idea of the content.
- H2 – Subheadings that categorize the key points within paragraphs and create divisions between sections. It is advisable to include semantic keywords related to the main idea expressed in the H1, as this helps both search engines and readers navigate the content effectively.
- H3 – Subsections that provide additional clarification and elaboration on the points covered in the H2. Alternatively, they can be utilized for structuring lists or bullet points.
- H4 – Subsections that offer further clarification and detail to the information presented in the H3. Similarly, they can be used for organizing lists or bullet points.
Why are Header Tags Important for SEO?
Header Tags Help Users and Search Engines Understand Your Content
When search engines crawl your website, they look for header tags to help them understand the organization of your content. By using header tags, you provide a clear structure to your content, making it easier for both users and search engines to understand the context and relevance of different sections. This improves the overall readability and accessibility of your content.
Header Tags Improve User Experience
Well-structured content with properly formatted header tags enhances the user experience. Header tags are typically larger and more prominent than the rest of the text on a page, which makes them easy to scan. This can be helpful for users who are looking for specific information or who want to quickly get a general overview of the page.
This leads to higher engagement and a positive user experience, which can indirectly impact your SEO efforts.
Header Tags can Help You Rank for Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are the concise summaries of information that appear at the top of search engine result pages (SERPs). By using header tags strategically, you can provide clear and concise answers to specific questions, increasing your chances of being featured in these snippets. This can result in higher visibility and increased organic traffic to your website.
How To Improve Your SEO With Header Tags?
Use One H1 Header Tag Per Page
Each page on your website should have only one H1 tag, which represents the main heading or title of the page. This helps search engines understand the primary focus of the content and avoid confusion.
Make Sure Every Important Page Has an H1
Ensure that every important page of your website has an H1 tag. This includes landing pages, product pages, blog posts, and any other content that you want to optimize for search engines.
Use Headers To Break Up Text and Optimize Page Structure
Example of an organized page structure using header tags
Divide your content into logical sections using header tags. This helps break up long blocks of text, making it easier for readers to navigate and digest the information. Additionally, search engines give more weight to content within header tags, so using them strategically can improve keyword relevancy and overall page structure.
Optimize Header Tags with Keywords
Include relevant keywords within your header tags to help search engines understand the main topics covered in each section. However, make sure to use keywords naturally and avoid keyword stuffing, as it can negatively impact your SEO efforts.
Can I Use Multiple H1 Tags on a Page?
Using multiple H1 tags on a page is not recommended. It dilutes importance, confuses search engines, and disrupts hierarchy. Instead, use a single H1 tag for the main heading and employ other header tags for subheadings. This maintains clarity, improves SEO, and enhances user experience.
Can I style Header Tags Differently?
Styling header tags differently adds visual appeal to your web page. CSS provides flexibility to customize font size, color, weight, and spacing. You can make the H1 tag more prominent with a larger font size to grab attention. Get creative with styling while ensuring it complements your overall design.
Image Alt Texts
What are Image Alt Texts?
Image alt text, also known as alternative text or alt attribute, is a text description of an image that is used to provide alternative information for users who cannot see the image. This includes users who are visually impaired and use screen readers, as well as users who have slow internet connections and the image does not load properly.
Example of Descriptive Image Alt Texts
Why Are Image Alt Texts Important for SEO?
Alt Tags Are Fundamental For Accessibility And User Experience
While search engines cannot interpret images directly, they rely on alt texts to understand the content and context of an image. By providing descriptive alt texts, you make your website more accessible to visually impaired individuals, ensuring an inclusive user experience. Accessibility is not only important for ethical reasons but also helps search engines understand the relevance and value of your content.
Image Search SEO
Alt texts play a crucial role in optimizing images for search engine rankings. When you include relevant keywords and descriptions in your alt texts, it helps search engines better understand the content of the image and its relevance to the surrounding text or webpage. This improves the chances of your images appearing in image search results, driving additional organic traffic to your website.
Optimizing image alt text for Google Images
Image Alt Text Best Practices for SEO
Describe The Image And Be Specific
When crafting alt texts, it’s important to accurately describe the image while being specific. Provide concise yet meaningful descriptions that capture the essence of the image. For example, instead of using a generic alt text like “red car,” you could use “vibrant red convertible sports car driving along a scenic coastal road.” Specific and detailed alt texts not only help search engines understand the image but also provide a better user experience for visually impaired individuals.
Add Context That Relates To The Topic Of The Page
Consider the overall context of the webpage and ensure that your alt text is relevant to the topic or theme. The alt text should provide additional information that enhances the understanding of the content or complements the surrounding text. This helps search engines associate the image with the relevant keywords and improves the overall SEO of the page.
Keep Your Alt Text Fewer Than 125 Characters
While alt texts should be descriptive, it’s important to keep them concise and within a reasonable character limit. Most search engines recommend keeping alt texts under 125 characters. By being concise, you ensure that the alt text is displayed properly across different devices and doesn’t get cut off, providing a seamless user experience.
Don’t Start Alt Text With “Picture Of…” Or “Image Of…”
Starting alt texts with generic phrases like “picture of” or “image of” adds little value to the description and wastes valuable character space. Instead, focus on providing specific details about the image content itself. For example, instead of saying “image of a cat,” you could say “playful tabby cat chasing a ball.”
Include Relevant Keywords
Incorporating relevant keywords in your alt texts can improve your website’s visibility in image search results. Conduct keyword research to identify the most appropriate and high-performing keywords related to the image and the surrounding content. Use them naturally within the alt text while ensuring it remains descriptive and accurate.
Don’t Add Alt Text To Every Image
While alt texts are essential for accessibility and SEO, it’s important to use them judiciously. Not every image on your website requires an alt text. Decorative images, spacer images, or images that are purely aesthetic and don’t add any meaningful information can be left without alt texts. Focus on providing alt texts for images that contribute to the overall content and user experience.
Good Examples of Image Alt Texts
- Image of a cat sitting on a windowsill.
Alt text: “A cat sitting on a windowsill. The cat is white with black stripes.” - Image of a group of people hiking in the mountains.
Alt text: “A group of people hiking in the mountains. The mountains are covered in snow and the people are wearing hiking gear.” - Image of a food truck selling tacos.
Alt text: “A food truck painted in blue and white, and the tacos are on display in the window.” - Image of a book cover with the title “The Lord of the Rings.”
Alt text: “Book cover for the novel “The Lord of the Rings” by J.R.R. Tolkien. The cover image shows a landscape with mountains and a river.”
Bad Examples of Image Alt Texts
- IMG_1234.
- Untitled.
- Picture of a thing.
- Image.
- Screenshot.
How to Find Images with Missing Alt Text?
- Manual Review: Go through each page of your website and inspect the HTML code for image tags. Look for instances where the alt attribute is empty or missing.
- Accessibility Auditing Tools: Utilize accessibility auditing tools like WAVE, Axe, or Lighthouse, which can scan your website and provide reports on accessibility issues, including missing alt text for images.
- Content Management System (CMS) Plugins: If you use a CMS like WordPress, there are plugins available that can help identify and manage missing alt texts.
Can I Use The Same Alt Text For Multiple Similar Images?
While it may be tempting to use the same alt text for similar images, it’s generally recommended to provide unique alt texts for each image. Alt texts should accurately describe the content of each individual image, even if they are similar.
For example, if you have two images of a cat, you could use the same alt text for both images: “This is a picture of a cat.” However, if one image is of a cat sitting on a windowsill and the other image is of a cat playing with a ball of yarn, you should use different alt text for each image. You could use the following alt text for the first image: “This is a picture of a cat sitting on a windowsill.” And the following alt text for the second image: “This is a picture of a cat playing with a ball of yarn.”
This allows search engines to differentiate between the images and understand their context.
Can I Use Alt Text For Non-Image Elements Like Icons Or Buttons?
Alt text is primarily used to provide a textual description of an image for users who are visually impaired or have difficulty viewing images.
When it comes to icons or buttons, you should consider their context and purpose. If the icon or button is purely decorative and does not convey any meaningful information, it is generally not necessary to include alt text. Decorative images are often better handled using CSS background images or other styling techniques.
However, if the icon or button has a functional or informational role, such as indicating a specific action or providing important information, it is important to include appropriate alt text so that users with visual impairments can understand its function.
WANT DIGITAL INSIGHTS STRAIGHT TO YOUR INBOX?
Internal Links
What are internal links?
Internal links are hyperlinks that connect one page on a website to another page within the same domain. They play a crucial role in website navigation and user experience by allowing visitors to easily navigate through different pages of a website. Unlike external links that point to other websites, internal links keep users engaged within the same website, guiding them to relevant information and helping them discover more content.
Internal links vs external links
While internal links connect pages within the same website, external links are hyperlinks that lead users to different websites. Internal links are essential for enhancing the website’s structure and usability, providing a smooth and seamless browsing experience for visitors. On the other hand, external links can be valuable for referencing authoritative sources and providing additional information or references to readers. Both internal and external links contribute to the overall SEO strategy of a website, but they serve different purposes.
Different Types of Internal Links
Contextual Links
Contextual links are hyperlinks that are embedded within the body content of a webpage. They are usually placed strategically within the text to provide additional information or direct readers to related topics or pages. Contextual links are valuable for enhancing the user’s understanding of the content and encouraging them to explore more relevant information.

Navigational links
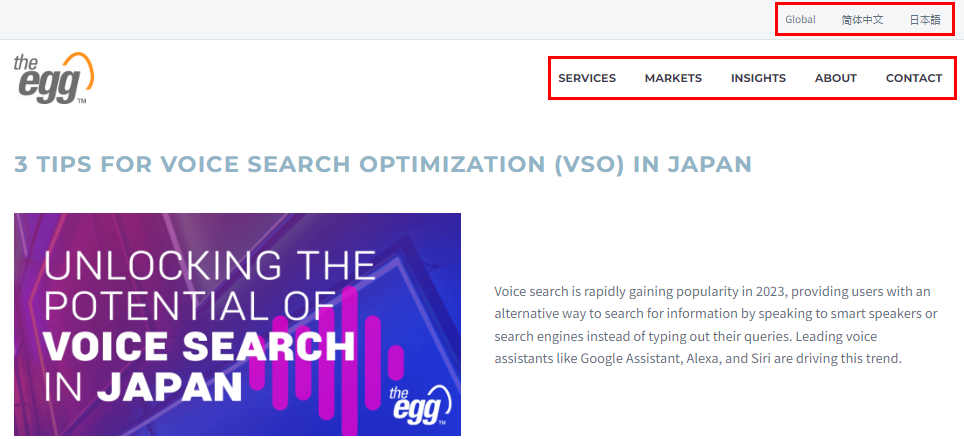
Navigational links, also known as site navigation or menu links, are typically located in the header, footer, or sidebar of a webpage. They provide a structured and organized way for users to navigate through different sections or categories of a website. Navigational links often include dropdown menus or submenus, allowing visitors to access specific pages or sections directly.
Why are Internal Links Important to Google?
Internal Links Establish Relationships Between Content
Internal links help search engines understand the relationships between different pages on your website. By linking related content together, you provide search engines with a clear indication of the relevance and importance of each page. This allows search engines to better organize and index your website, improving its visibility in search results.
Internal Links Help Search Engines Better Find Your Content
When search engine crawlers visit your website, they follow internal links to discover and index new content. By strategically placing internal links throughout your website, you ensure that all your pages are accessible to search engines. This increases the chances of your content being discovered and ranked in search results.
Internal Link Distribute Authority (Link Juice) Between Pages
Internal links play a role in distributing authority, also known as link juice, between different pages of your website. When a page with high authority links to another page, it passes some of its authority to the linked page. This helps improve the ranking potential of the linked page and increases its visibility in search results. Internal linking can be an effective way to boost the visibility and authority of important pages on your website.
How to Build Your Internal Linking Strategy for SEO?
Identify Your Site’s Pillar Pages
Start by identifying the pillar pages on your website. These are the main pages that cover broad topics or categories and serve as the foundation of your content. Pillar pages are typically comprehensive and link to more specific subtopics or related pages.
Create Topic Clusters Using Internal Links
Organize your content into topic clusters by creating internal links between the pillar page and its corresponding subtopics. The pillar page acts as the central hub that links to all the relevant subtopics, and each subtopic links back to the pillar page. This helps search engines understand the topical relevance and hierarchy of your content.
Link High Authority Pages to New Pages
When you create new content, ensure that you link it to relevant high authority pages on your website. By doing so, you pass some of the authority from the high authority pages to the new page, giving it a better chance of ranking in search results. This strategy helps new pages gain visibility and improves the overall SEO performance of your website.
Use Descriptive, Keyword-rich Anchor Texts
When creating internal links, use descriptive and keyword-rich anchor texts. Anchor texts are the clickable words or phrases that are linked to another page. By using relevant keywords in your anchor texts, you provide additional context to search engines about the content of the linked page. This can help improve the page’s visibility for specific keywords in search results.
Monitor and repair broken Links
Regularly monitor your website for broken links and repair them promptly. Broken links can negatively impact user experience and SEO. Use tools or plugins to identify broken links and update or redirect them to the appropriate pages. By ensuring that all your internal links are functional, you provide a seamless browsing experience for visitors and maintain a healthy website structure.
How many internal links should I have on a page?
The number of internal links on a page can vary depending on the content and structure of your website. There is no specific number that applies universally. However, it’s important to ensure that your internal links are relevant, helpful, and not excessive or spammy.
Does Link Sculpting Still Work?
Link sculpting, which refers to the practice of manipulating internal links to influence the flow of link juice within a website, is not as effective as it used to be. Search engines have evolved to better understand and handle internal links, making link sculpting less impactful in terms of SEO.
Should I Prioritize Internal Linking Within Content Or Navigation Menus?
Both internal linking within content and navigation menus are important. Content-based internal links provide contextual relevance and guide users to related information. Navigation menus, on the other hand, offer a structured way for users to navigate through your website. Prioritize a balanced approach by using both effectively.
Are There Any Tools To Analyse Internal Link Structure?
Yes, there are tools available to analyze internal link structure. Some popular tools include Ahrefs, Moz, and SEMrush. These tools can provide insights into the number of internal links, broken links, anchor text usage, and other metrics related to your internal link structure.
How To Fix Internal Links Contain Nofollow Attribute?
If your internal links contain the “nofollow” attribute, it means search engines won’t follow those links or pass authority through them. To fix this, you’ll need to remove the “nofollow” attribute from the internal links. Review your website’s settings, CMS, or plugins to ensure that internal links are not marked with the “nofollow” attribute. Update the links accordingly to allow search engines to follow them and pass authority.
External Links
External links are a type of hyperlink that points to a website or web page that is hosted on a different domain name.
Example of External Linking, source: mageplaza
How do External Links Help with SEO?
External Links Improve your Credibility
When you include external links in your content, you provide your readers with additional resources and references to support your claims. By linking to reputable websites that offer valuable information related to your topic, you establish credibility and demonstrate that you’ve done thorough research. Search engines take note of this and view your content as trustworthy, which can positively impact your search rankings.
External Links Improve your Content’s Relevancy
External links help search engines understand the context and relevance of your content. When you link to authoritative sources that are relevant to your topic, you signal to search engines that your content is valuable and aligned with the subject matter. This can contribute to higher visibility in search results and increase your chances of attracting organic traffic.
External Linking Best Practices for SEO
Now that we understand the significance of external links, let’s discuss some best practices to optimize their impact on your SEO efforts.
Link To Reputable Sources
When choosing external sources to link to, prioritize reputable websites with high domain authority. Linking to trustworthy sources not only adds credibility to your content but also helps search engines recognize the quality and relevance of your website.
Use Anchor Text Correctly
Anchor text is the clickable text that appears in a hyperlink. It’s crucial to use relevant and descriptive anchor text that accurately reflects the content you are linking to. This helps search engines understand the context of the link and improves the user experience.
Open External Links in A Different Tab
To prevent users from navigating away from your website, it’s recommended to set external links to open in a new tab or window. This way, visitors can explore the linked content without leaving your site, ensuring a seamless browsing experience.
Do Not Link to Competing Websites
While external links are beneficial, it’s important to avoid linking to direct competitors. Instead, focus on linking to complementary sources that enhance the user experience and provide additional value to your audience.
Nofollow or Follow External Links?
When it comes to external links, you may encounter the terms “nofollow” and “follow.” These terms determine whether search engines should follow the link and attribute ranking signals to the linked page. While follow links pass authority and contribute to search rankings, nofollow links do not.
In general, it’s recommended to use a combination of both follow and nofollow links. Follow links help with SEO and credibility, while nofollow links provide a natural balance and prevent potential issues with spam or low-quality links.
Is Too Many external links bad for SEO?
While external links are beneficial for SEO, it’s important to maintain a balance and avoid excessive linking. Search engines evaluate the quality and relevance of your external links, so if you have too many low-quality or irrelevant links, it can negatively impact your SEO efforts.
Focus on incorporating external links that genuinely add value to your content and enhance the user experience. Quality over quantity is key when it comes to external linking.
URL Structure
Anatomy of A URL
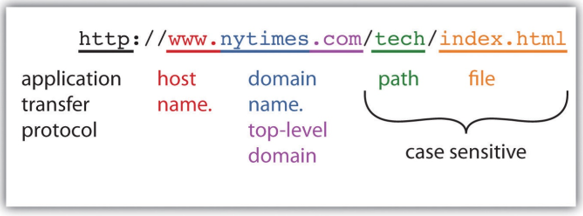
A URL consists of several components that work together to provide a precise address for a webpage. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
- Protocol: The protocol specifies the communication method used between the user’s browser and the server hosting the website. The most common protocol is “http://” or its secure counterpart, “https://”.
- Domain: The domain is the main part of the URL that identifies a specific website. It usually begins with “www.” but can sometimes omit it.
- Path: The path is the specific location within the website’s structure that leads to a particular webpage. It often includes directories and subdirectories, forming a hierarchical structure.
- Query Parameters: Query parameters are optional elements that provide additional information to the server, usually for dynamic content or search functionality. They appear after a question mark “?” in the URL.
Now that we understand the different parts of a URL, let’s explore why URL structure matters for SEO.
Why does URL Structure Matter for SEO?
Improved User Experience
A well-structured URL enhances user experience by providing clear and meaningful information about the webpage’s content. Users can quickly grasp what to expect from the page just by looking at the URL.
A concise and descriptive URL helps users navigate your website more efficiently, leading to a positive user experience.
Improved Organic Rankings
Search engines consider the URL structure as one of the ranking factors when determining the relevance and quality of a webpage. A clean and logical URL structure makes it easier for search engine crawlers to understand and index your content.
When your URLs align with the overall content and site structure, it positively impacts your website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
How to Create A SEO-friendly URL Structure?
Standardize Your URLs In Lowercase
Consistency is key when it comes to URL structure. Always use lowercase letters to ensure uniformity across your website. Mixed-case URLs can create confusion and lead to duplicate content issues.
Use Hyphens, Not Underscores
When separating words in a URL, use hyphens instead of underscores. Search engines interpret hyphens as word separators, making it easier for them to recognize individual words in the URL. Underscores, on the other hand, can be perceived as a single word, hindering readability.
Keep It Short and Sweet
Shorter URLs are not only easier for users to remember and share but also tend to perform better in search engine rankings. Aim for concise URLs that accurately reflect the page’s content without unnecessary complexity or irrelevant information.
Insert Relevant Keywords
Including relevant keywords in your URL can give search engines additional context about the content on the page. However, avoid keyword stuffing and ensure the keywords appear naturally within the URL.
Avoid Use of URL Parameters
URL parameters, such as session IDs or tracking codes, can create duplicate content issues and confuse search engines. If possible, avoid including unnecessary parameters in your URLs.
Future Proof Your URLs
Consider creating URLs that are flexible and adaptable to any potential future changes in your website’s structure. This ensures that even if you reorganize or modify your site, the URLs remain consistent and functional.
Example of SEO-friendly URLs
- https://www.theegg.com/seo/apac/
Starts with the domain “theegg.com” and then proceeds with the path “/seo/apac/”. This URL indicates that the website belongs to The Egg, and specifically focuses on SEO (Search Engine Optimization) in the APAC (Asia-Pacific) region. By including relevant keywords like “seo” and “apac” in the URL, it helps search engines and users understand the specific topic and geographical focus of the webpage.
- https://www.theegg.com/seo/apac/how-to-use-chatgpt-for-seo
Starts with the domain “theegg.com” and then proceeds with the path “/seo/apac/how-to-use-chatgpt-for-seo” which provides a clear and logical structure. It indicates that the webpage is related to SEO, specifically in the APAC region. The subsequent path segment, “how-to-use-chatgpt-for-seo,” is descriptive and includes relevant keywords that highlight the content’s topic on ChatGPT.
In these examples, the URLs are descriptive, include relevant keywords, and provide a clear hierarchy of the website’s content.
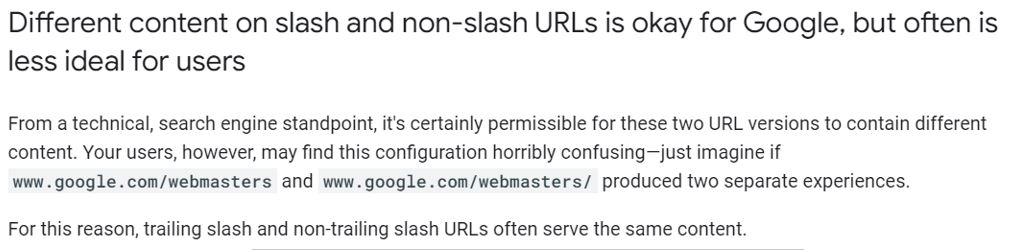
Trailing Slash or No Trailing Slash
Google’s stand on Trailing Slash or No Trailing Slash
The use of a trailing slash at the end of a URL is a matter of personal preference and doesn’t directly impact SEO. However, consistency is important. Choose either a trailing slash or no trailing slash and ensure that all internal and external links on your website follow the same convention. This avoids potential confusion and keeps your URL structure clean and uniform.
Schema Markup
What Is Schema Markup?
Schema markup, also known as structured data, is a type of code that you can add to your website to provide search engines with additional information about your content. It uses a specific vocabulary of tags that help search engines understand the context and meaning of the data on your webpages. This, in turn, enables search engines to display more relevant and informative results to users.
The difference between Schema.org, microdata, and structured data
Schema.org is a collaborative project launched by Google, Bing, Yahoo!, and Yandex. Its purpose is to create a universal vocabulary for structured data markup.
Microdata, on the other hand, is a specific syntax used to implement schema markup.
Structured data is a broader term that encompasses various formats, including microdata, JSON-LD, and RDFa.
Benefits of Schema Markup for SEO?
Now that we understand what schema markup is, let’s explore its benefits for SEO.
Helps Search Engines Better Understand Your Content
By implementing schema markup, you provide search engines with valuable context about your content. This allows them to accurately interpret the purpose, meaning, and relationships of different elements on your webpages. As a result, search engines can better match your content to relevant user queries, improving your visibility in search results.
Helps You Stand out in Search with Rich Results
Schema markup enables the creation of rich results, also known as rich snippets or enhanced listings, which provide additional information directly in search engine results pages (SERPs). Rich results can include star ratings, pricing information, images, and other details that make your listing more appealing and informative.
By standing out in search, you increase the chances of attracting clicks from users and driving more organic traffic to your website.
Common Types of Schema Markup
Organization Schema Markup
Example of Organization Schema Markup
This type of markup provides details about your organization, such as its name, logo, contact information, and social media profiles. It helps search engines display accurate and comprehensive information about your business.
Local Business Schema Markup
Example of Local Business Schema markup
If you have a physical store or business location, local business schema markup is essential. It includes details like your address, phone number, opening hours, and customer reviews. It improves your visibility in local search results.
Product & Offer Schema Markup
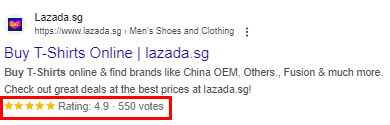
If you sell products or services online, product and offer schema markup can enhance your listings in search results. It allows you to provide information such as pricing, availability, and customer reviews, making your offerings more enticing to potential customers.
Breadcrumbs Schema Markup
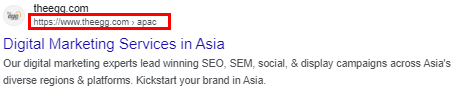
Breadcrumbs are a navigational aid that helps users understand the structure of your website and easily navigate between different pages. Breadcrumbs schema markup adds this functionality to your site, improving user experience and search engine visibility.
Article Schema Markup
If you publish articles or blog posts, implementing article schema markup can help search engines understand the structure and key elements of your content. It can also enable features like displaying the publication date, author, and headline in search results.
Video Schema Markup
Example of Video Schema Markup
Video schema markup provides search engines with information about your videos, such as the title, description, duration, and thumbnail image. This can lead to enhanced video snippets in search results, increasing visibility for your video content.
How Do I Test And Verify My Schema Markup?
Once you’ve implemented schema markup on your website, it’s crucial to test and verify its correctness. Google provides a free testing tool – Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool. It allows you to enter a URL or paste the code snippet and validates the markup, ensuring that it meets the required standards and is error-free.
How Do I Implement Schema Markup On My Website?
Implementing schema markup on your website can be done manually or by using plugins or tools. If you’re comfortable with coding, you can add the schema markup directly to your HTML code.
Alternatively, many content management systems (CMS) offer plugins or built-in options that simplify the implementation process. For example, WordPress users can leverage plugins like Yoast SEO or Rank Math, which provide easy-to-use interfaces for adding schema markup to their websites.
Wrapping Up
In summary, on-page SEO is a critical component of any successful digital marketing strategy. By optimizing various elements of your website’s pages, you can improve your search engine rankings, increase organic traffic, and enhance the overall user experience.
Keep in mind that on-page SEO is an ongoing process, and it requires constant monitoring, testing, and refinement. As search engine algorithms evolve, staying up to date with the latest best practices is essential to maintain and improve your website’s visibility and rankings.
So, make on-page SEO a priority in your digital marketing strategy, and watch as your website rises in search engine rankings, engages visitors, and achieves long-term success.