A Complete Guide to Google SERP Features
Google consistently updates its SERP features to optimize the search experience.
Google’s SERP features are special elements that offer greater real estate for your content to occupy when people search your keywords. Thus, optimizing your site to rank for Google’s rich results will give you greater SERP visibility.
Read on to discover the nine most common Google SERP features—and how they work—so that you can rank for them and increase your click-through rates (CTR).
What is a SERP?
A search engine results page (SERP) appears after a user submits a search query on a search engine. SERPs typically display links to websites that the respective search engine’s algorithm deems most relevant to a search query. And in addition to organic results, which are traditionally displayed as links, SERP features also regularly appear on the page.
What are the changes to Google’s SERP layout with SGE?
Google has recently introduced a new feature called SGE (Search Generative Experience) that has transformed the SERP layout. SGE adds an interactive AI-powered snippet at the top of the results page that provides an answer to the user’s query. The snippet also includes a carousel of websites that SGE used to corroborate the response. The snippet may take a few seconds to generate as the AI algorithms are at work.
This new layout is designed to provide users with a more helpful and informative experience. It is still in the early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with search engines.
What is a SERP Feature?
SERP features go beyond traditional organic results. They help users see the information they need–which is hopefully your site content–directly on the SERP based on relevance to the query.
The nine most common SERP features–in no particular order–are:
- Rich snippets
- Featured snippets
- People also ask
- Image packs
- Local packs
- Videos
- Knowledge graphs
- Sitelinks
- Paid results
Check out APAC in 3 (EP 10) for a visual guide to these common Google SERP features.
And for a deeper dive, read the full article below.
WHY ARE SERP FEATURES IMPORTANT?
Before delving into the complexities of SERP features and investing great efforts in trying to rank for them, we must initially answer the critical question: Why are SERP features important?
SERP features’ most pronounced advantage is the increased real estate they command on search results pages, which allows your website to distinctly stand out amidst the competition. Given users’ preference for immediate, effortless answers to their queries, your results prominently being displayed as SERP features can lead to an increased click-through rate, driving more traffic to your site.
Furthermore, by integrating diverse formats, SERP features adapt to different user preferences, providing the most effective responses to users’ queries. For instance, a text featured snippet may be sufficient to explain the difference between a CV and a resume, whereas a video is better suited to demonstrate how to bake a cake.
Ultimately, if your website prominently appears as SERP features on search result pages, it signals users that Google has validated your site as a reliable and authoritative source. Consequently, this not only amplifies brand awareness but also fosters trust with your users.
WANT DIGITAL INSIGHTS STRAIGHT TO YOUR INBOX?
9 Common Google SERP Features AND HOW TO TARGET THEM
Here, let’s explore nine of the most common Google SERP features and how they work.
What Is A Google Featured Snippet?
Featured snippets appear as boxes at the very top of the SERP providing short, instant answers to a user’s search query. They can come in various formats—like short paragraphs, bulleted or numbered lists, images, or widgets—and are common for search terms inquiring about facts, famous people, events, unit conversions, calculations, and more.
How to Target a Featured Snippet
Give details of immediate practical importance related to your keywords that directly add value and answer queries.
Queries that typically trigger featured snippets often focus on the five ‘W’s and one ‘H’: who, where, what, why, when, and how. To align with this and ensure Google recognizes your content as a potential direct answer, structure your content around these cardinal question words and integrate them into your headings and subheadings.
Secondly, it’s essential to ensure your content is easily comprehensible. Considering that featured snippets aim to provide straightforward answers to users, Google may overlook content that utilizes long sentences and complicated vocabularies. Tools such as Hemingway Editor can significantly enhance the readability of your content.
Beyond standard paragraphs, lists and tables are also common forms of featured snippets. Format your content in these two forms when applicable and make sure you use the correct HTML markups.
Featured Snippet Example
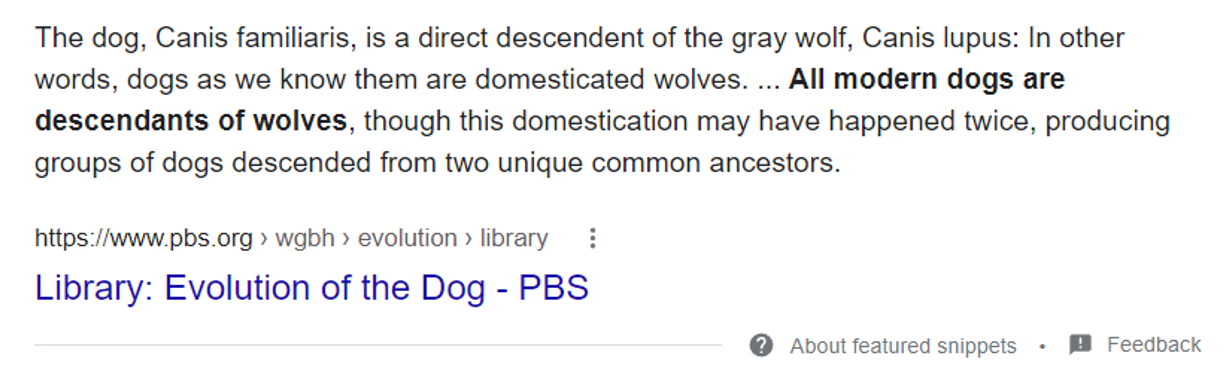
What Is A Google Rich Snippet?
Basic organic and paid results consist of a title, description, and a link to a particular domain’s webpage. And rich snippets are additional information—like reviews, ratings, price, and stock availability—that appear below the basic elements and can play a role in swaying users to click on the result.
Schema markup helps search engines better identify rich snippet information within your content and improves the likelihood of that information appearing on the SERP.
How to Target a Rich Snippet
Implement schema markup, which is backend code that Google can parse to surface information on the SERP. Google supports JSON-LD and Microdata for structured data, with more details available in Google’s web developer documentation. After you implement structure data, do not forget to validate it using Google’s Rich Results Test.
Rich Snippet Example
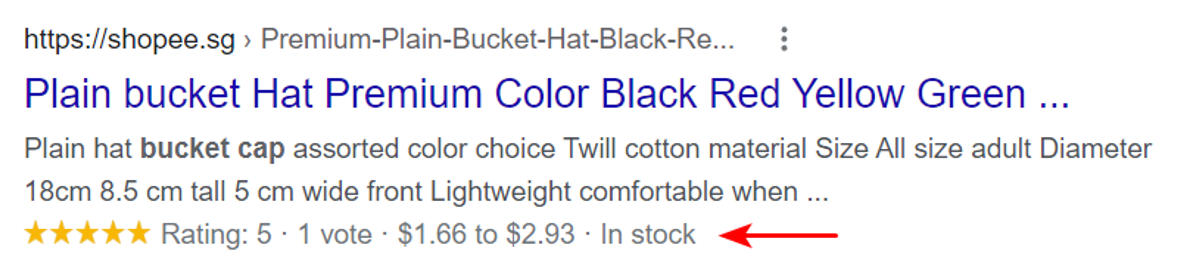
What Is Google People Also Ask?
People also ask is a list of questions that Google believes can answer any related questions users might have about a search query or topic. The section features accordion-style navigation, so by clicking on a question, you can view its answer from a reliable external source in the drop-down.
How to Target People also ask
Research shows that ‘People also ask’ features are triggered by question-based queries a staggering 86% of the time. Therefore, incorporating a Q&A format in your content and integrating questions relevant to search keywords can enhance your chances of appearing in this feature. Tools such as AnswerThePublic and AlsoAsked are great ways to generate ideas for commonly asked questions related to your topic. Alternatively, you can look at the questions in the current ‘People also ask’ feature and include them in your content.
People also ask Example
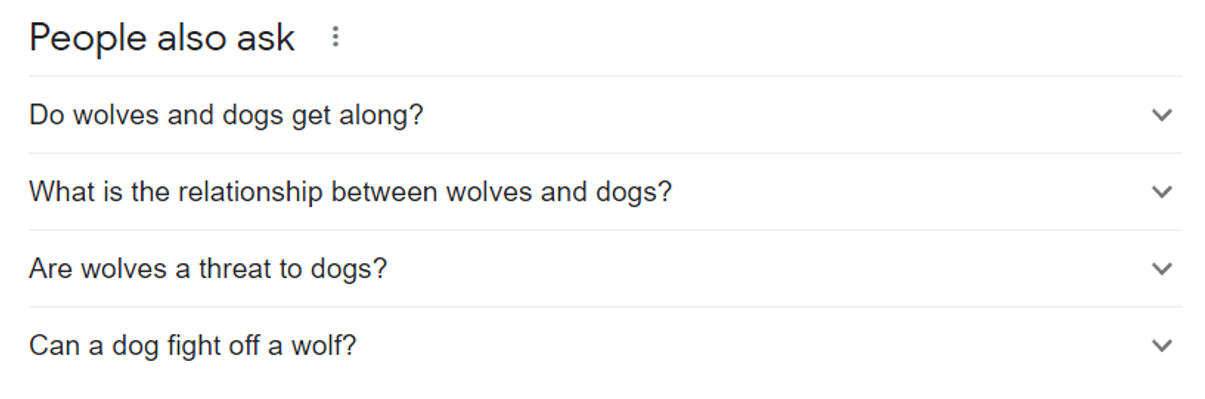
What Is A Google Image Pack?
Image packs are horizontal rows or blocks of images with links. Clicking on an image will bring you to Google Images, where you can click through to the website that’s hosting the image.
How to Target an Image Pack
Assign a caption and alt text to your images and ensure their file names are descriptive and relevant to the search query. It is equally beneficial to include your primary keywords in the alt text, improving the image’s relevance to the search query.
Add images to your sitemap to help Google discover them, thereby increasing the chances of them appearing as SERP features. Lastly, if you have an eCommerce store, consider adding structured data to your product images. This provides Google with a clearer understanding of not only the content and quality of your images but also their relation to the webpage, further assisting you to target SERP features.
Image Pack Example
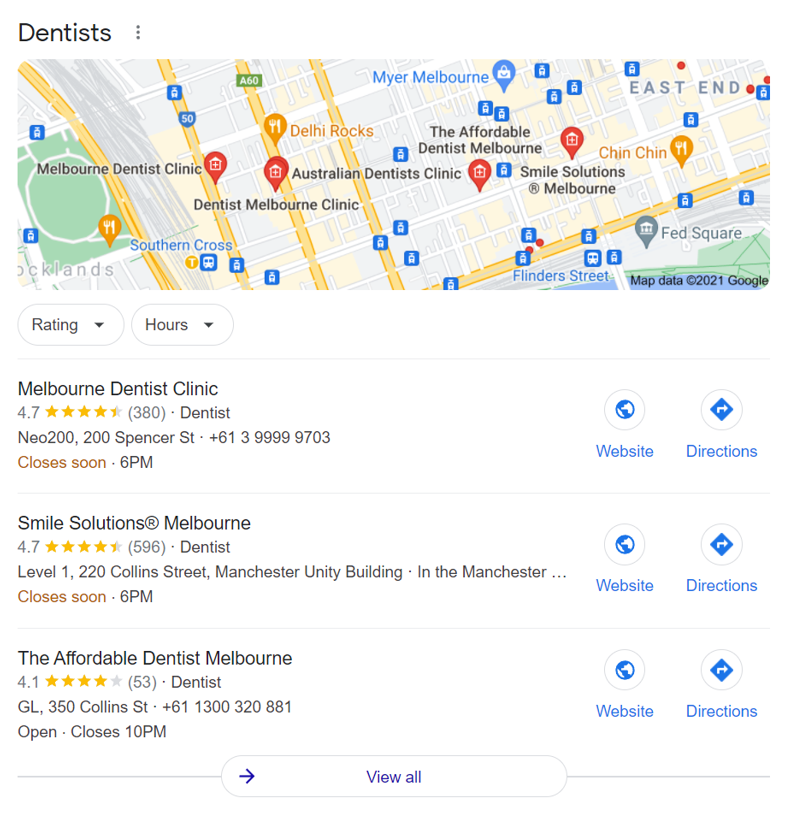
What Is A Google Local Pack & Teaser Pack?
For geographically defined search terms (e.g., “dentists in Melbourne”), Google’s SERP displays local packs with business locations it finds most relevant to a user’s search query, along with a Google map pinpointing their addresses.
And just below local packs, local teaser packs display additional business information— like operating hours, user reviews, contact details, prices, and images—of up to three local businesses showing on the Google map.
How to Target a Local Pack
To start, complete all fields in your Google Business Profile, including details such as photos, menu items, descriptions, categories and service lines. High quality photos that showcase your business location and services have the potential to boost user engagement with your listings. Furthermore, it’s imperative to keep information in your GBP current, particularly operational details like opening hours.
Secondly, optimize the relevant webpages with hyper-local content. Focus on providing quality content distinct to each location and make sure that you use location-specific terms in your metadata, headings, image alt txt and text.
Lastly, reputation management is essential. Achieve this by vigilantly monitoring and promptly responding to reviews. While positive reviews are clearly beneficial, negative reviews provide an opportunity to address customer dissatisfaction and restore trust. Taking the time to thoughtfully respond to feedback, particularly negative, can greatly enhance customer experience and plays a pivotal role in your website’s local pack ranking success.
Local Pack Example
Google SERP: Local packs and local teaser packs for the search term “dentists in Melbourne”
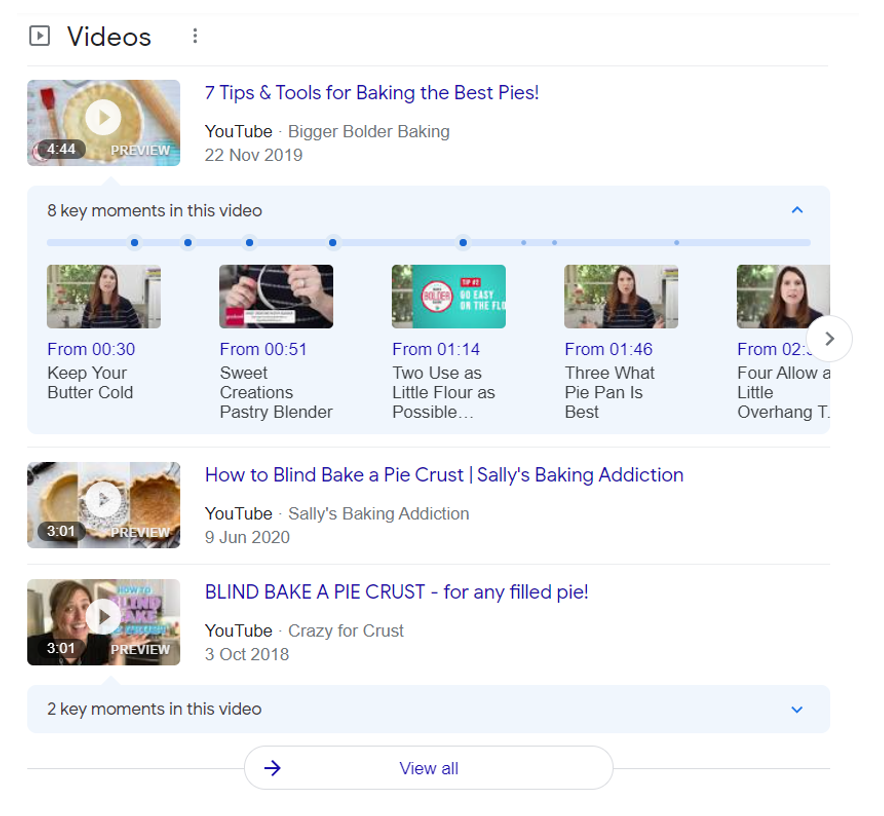
What Is A Google Video Result?
Video results may appear on a SERP if Google determines that videos would be the most appropriate and relevant content format to answer a user’s search query. Google may sometimes indicate the exact timestamps in a video that directly answers a search query, making for an overall better user search experience.
Most of the videos ranking on Google are hosted on YouTube (also owned by Google) and typically require schema markup for them to appear on SERPs.
How to Target a Video SERP Feature
Optimize video titles, descriptions, and tags with relevant keywords and provide an engaging video thumbnail. Meanwhile, incorporating key moments in your video content can also boost its potential to secure a SERP feature spot. By leveraging this strategy, your content can occupy more SERP real estate, leading to an improved click-through rate. Additionally, implement schema markup for the version on your site and ensure your video is also optimized on YouTube, which is owned by Google.
Video SERP Feature Example
Google SERP: Video results for the search term “bake a pie”
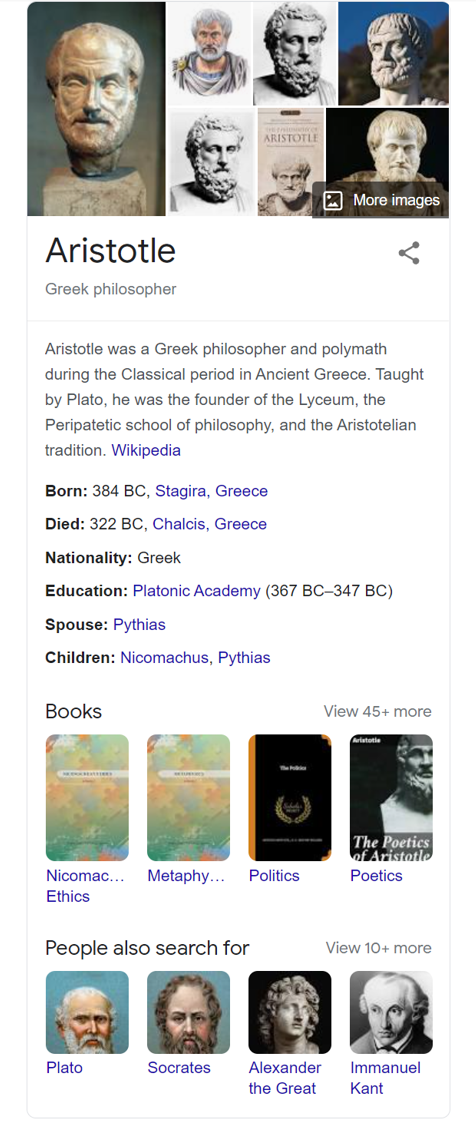
What Is A Google Knowledge Graph?
Knowledge graphs (or knowledge panels) extract and collate semantic data from various sources about a particular subject. The information is then displayed in a panel at the top of the SERP for mobile or to the right of search results on desktop, giving users most of the information they need about their query at a glance.
How to Target a Knowledge Graph
Although the information displayed in Google’s Knowledge Graph is at the search engine’s discretion, there are ways by which we can influence the outcomes. Firstly, implement structured data for your website and create your Google Business Listing. Ensure your brand, product, and service information is factual, accurate, and complete across the web (including structured data markup and GBP) so that Google can find and amalgamate it in a knowledge graph. Lastly, make sure all your social media accounts are verified and active, as Google may also rely on them to retrieve information for Knowledge Graph.
Knowledge Graph Example
Google SERP: Knowledge panel for the search term “Aristotle”
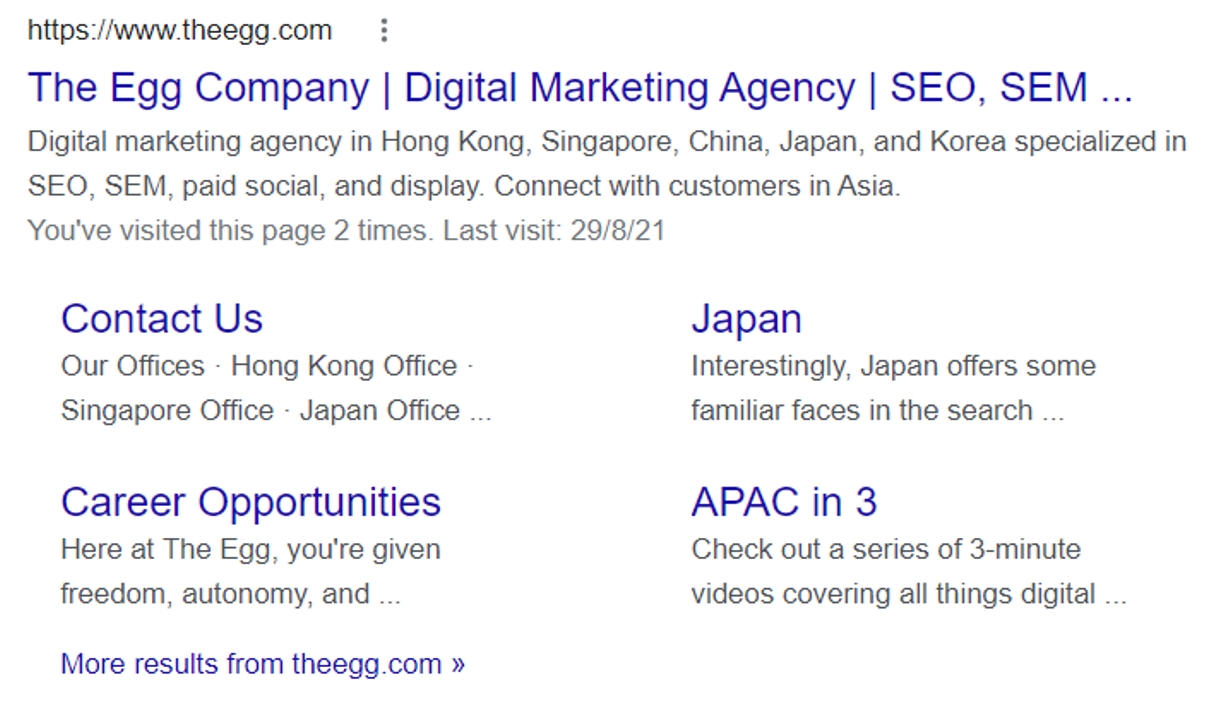
What Is A Google Sitelink?
Sitelinks are sets of up to 10 internal links directing users to specific landing pages on a website or sections on a page. Sitelinks will usually appear for branded searches, such as “The Egg Company” (that’s us!).
Besides occupying more SERP real estate and improving CTR, sitelinks can help users jump to specific pages they are interested in or navigate webpages for the information they want.
How to Target Sitelinks
Choose appropriate anchor text and link to important pages from your homepage to help Google understand your site structure and feature key pages. This in-depth guide will give you seven tips for getting Google sitelinks (plus 1 bonus tip!).
Sitelinks Example
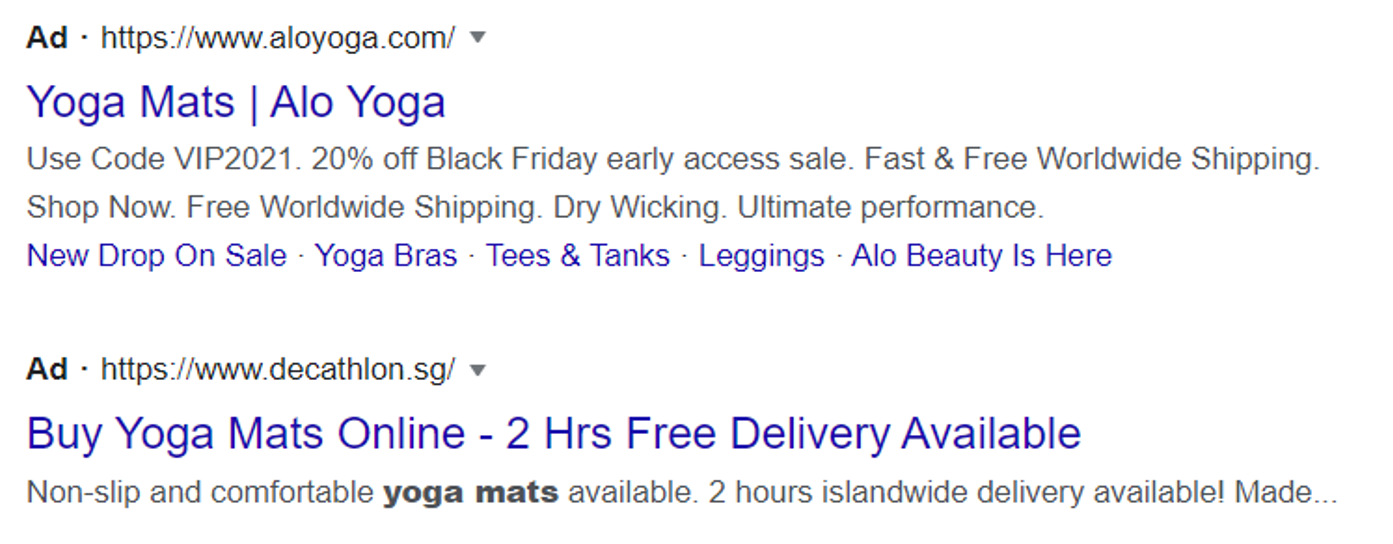
What Is A Google Paid Result?
Paid results are ads that appear at the top or bottom of a SERP and can be identified by the Ad tag. Paid results appear on SERPs based on several factors, including relevance to the search query, bid strategy, and more.
Note that paid results at the top of a SERP can push organic results further down the page and potentially impact their CTRs.
How to Target Paid Results
Through your Google Ads account, create compelling ads that are relevant to queries and optimized to convert. Leverage the use of ad extensions to gain greater visibility and provide users with additional information. It’s also necessary to constantly monitor, assess, and optimize your campaigns for better performance – this can be achieved by analyzing performance metrics, adjusting bid amounts, and conducting A/B tests.
Paid Results Example
BONUS: HOW TO TARGET SGE?
Google’s recent introduction of SGE (Search Generative Experience), which integrates Generative AI into search, offers novel opportunities for content optimization. As noted by SEO expert Lily Ray, direct content optimization for SGE is possible. As demonstrated in her video, Ray compiled a set of frequently asked questions about herself and provided direct responses on her website. When re-running those search queries after a week or two, SGE was directly sourcing content from her website.
Further tactics to influence SGE include the implementation of structured data markup, designed to enhance Google’s understanding of your site, ensuring data reliability and consistency across all web platforms, and the incorporation of rich media. The last element serves to increase the likelihood of Google sourcing the most fitting content format from your site.
However, it’s crucial to note that as SGE is in its nascent stage, the methods to target and influence it are subject to regular change. It’s essential to consistently monitor and analyze current SGE content to inform your content optimization strategies..
***
final words
Zero-click searches are increasing on Google, making it crucial for brands to optimize their websites and webpages for maximum SERP exposure and, therefore, brand visibility.
Aside from the SERP features mentioned above, less common ones for Google shopping, news, sports, jobs, reviews, breadcrumbs, and twitter cards may also appear if Google deems them relevant for a specific search query.
However, remember that Google frequently tests existing SERP features while introducing new ones, so it is imperative to stay up-to-date with these changes, learn how they may affect your SERP rankings, and leverage them as best as you can.